SMG Group provides professional and advanced complete iron making services, including plant design, construction, installation and commissioning of metal melting furnaces and subsequent technical guidance services. Since its inception, SMG Group has completed more than 200 metallurgical projects, and has rich experience in iron making, mastering the technology of mini and medium blast furnace, with the size range from 20m3 to 2000m3.

Sintering, which refers to the conversion of metallic powders into dense bodies - sintered metal, is a traditional manufacturing process before blast furnace iron manufacturing process. People have long used this process to produce ceramics, powder metallurgy, refractory materials, ultra-high temperature materials and so on. In the metallurgical process, it usually refers to the process of firing a series of physical and chemical changes in the material on the sintering equipment after mixing and pelleting a variety of powdered iron-containing raw materials, adding an appropriate amount of fuel and flux, and adding an appropriate amount of water before the blast furnace ironmaking production. In production, the belt type draft sintering machine is widely used to produce sinter ore. It mainly includes the preparation of sinter, batching and mixing, sintering and product treatment.
.jpg)
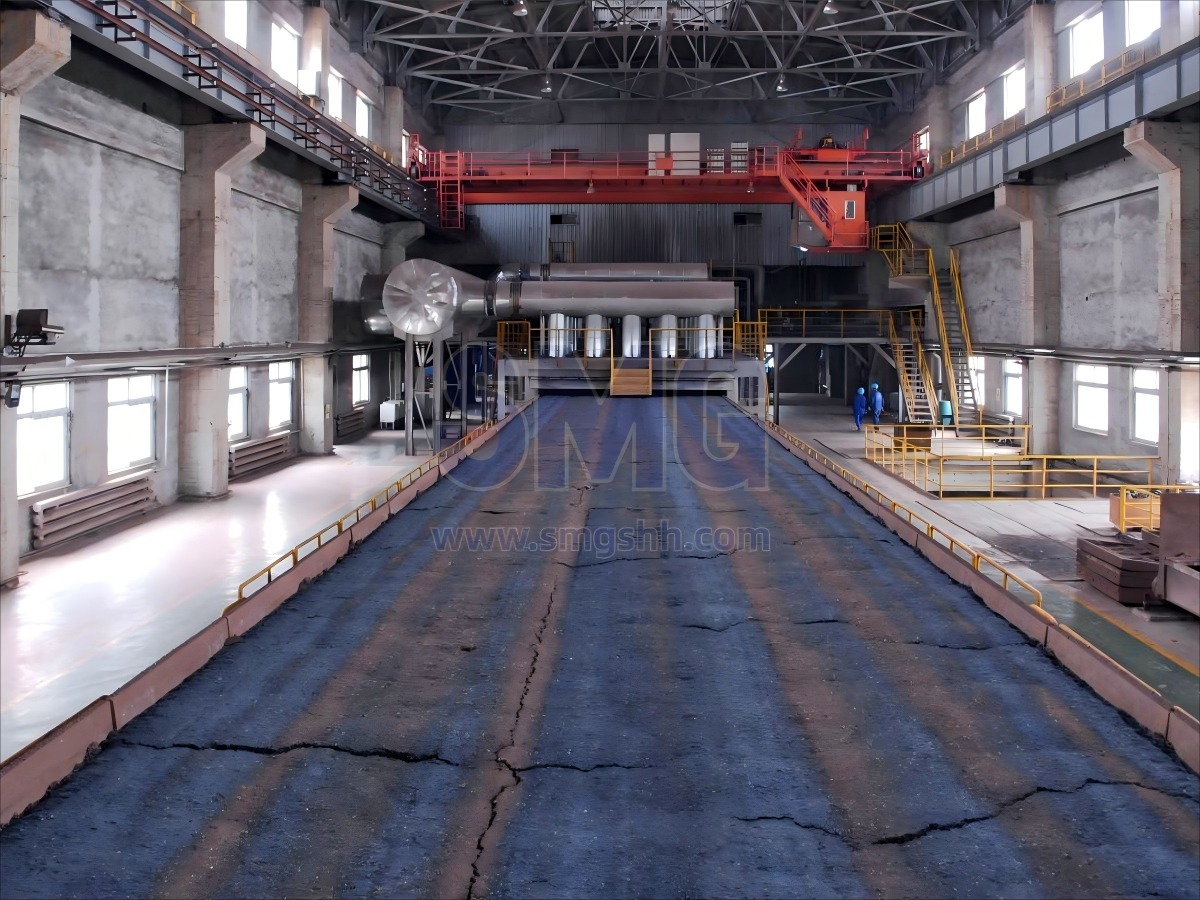
The sintering machine is used for the sintering operation of large ferrous metallurgy sintering plants, mainly for the sintering treatment of iron powder in large and medium-sized sintering plants.
.jpg)
It is the main equipment in the process of air extraction sintering, which can burn different components, different powder particle sizes of fine iron powder, rich ore powder into blocks, and partially eliminate the harmful impurities contained in the ore such as sulfur and phosphorus. The sintering machine is divided into several specifications of different lengths and widths according to the sintering area, and the user chooses according to its output or the site situation. The final yield is depending on the material sintering area. The larger the sintering area, the higher the yield.
The grate-kiln-cooler pelletizing process, a highly efficient method for producing iron ore pellet, primarily consists of several key sections: coal preparation system, raw material handling system, dry mixing system, pelletizing and induration system, and the grinding system.
The iron ore pellet production process can be summarized as follows: Prepared raw materials (including finely ground iron ore concentrate and additives) are proportioned and homogenized through dry mixing. This mixture then enters the pelletizing system to form green balls. These green balls are subsequently fed into the grate-kiln-cooler system for drying, high-temperature induration (roasting), and cooling, before finally being sent to the finished product handling system. Within this sequence, the high-temperature roasting stage in the rotary kiln is the most critical step, as it ultimately determines the final pellet quality and overall production capacity.
.jpg)
.jpg)

SMG Group intends to provide high quality blast furnace equipment and offer mature and complete blast furnace process from raw material to pig iron production.
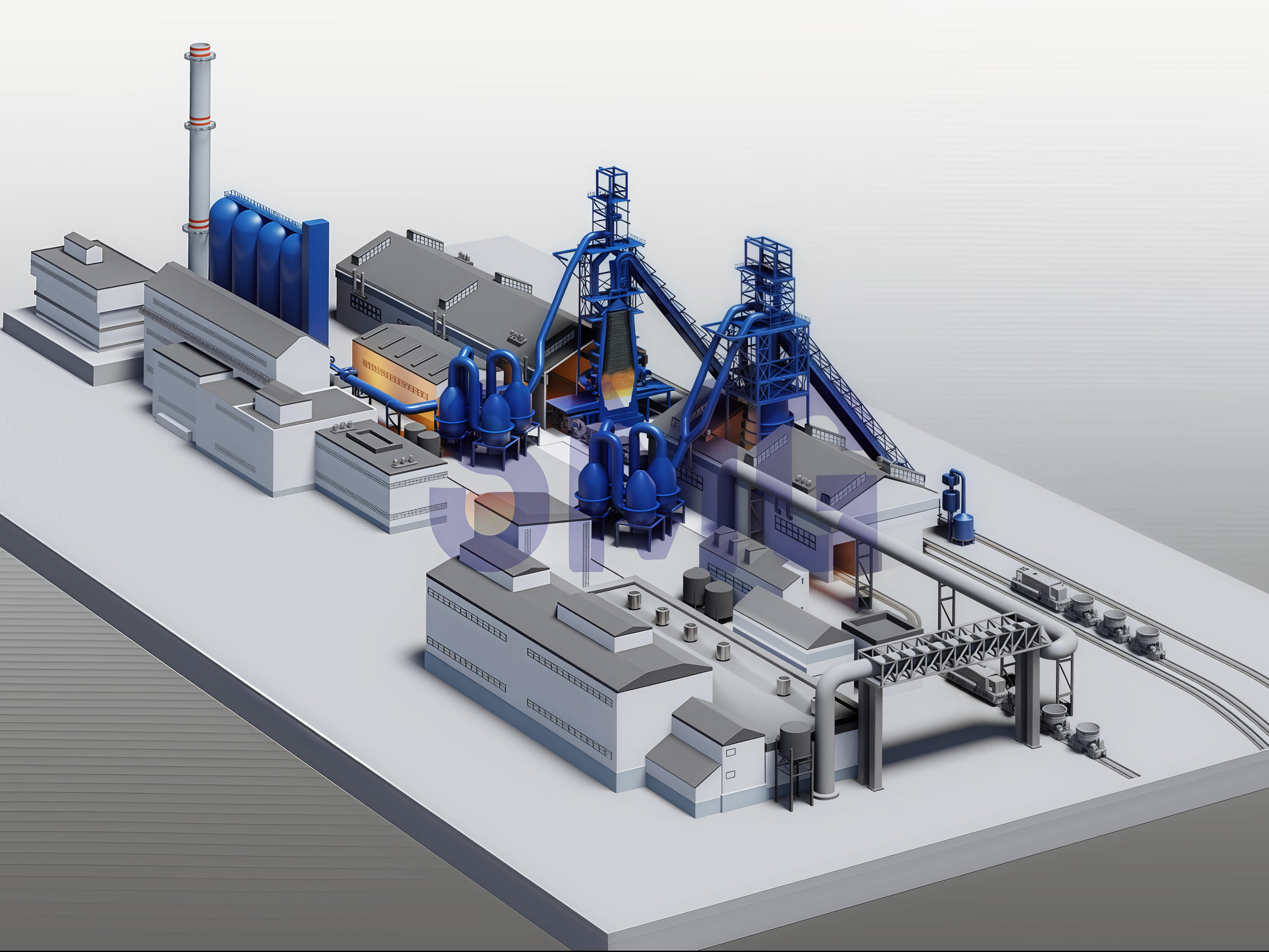
In general, the steel manufacturing process begins with ironmaking, which refers to the process of extracting iron from iron ore through a series of chemical reactions and physical treatment processes via iron smelting furnace - blast furnace. At present, the most common way to make iron is to produce iron in blast furnaces. Before entering the furnace, iron ore needs to undergo certain iron processing treatment, such as beneficiation, crushing, sintering, pelletizing and other processes, and iron ore can only be put into the blast furnace for smelting after meeting certain quality requirements and turned into molten iron and slag. The melting point of iron and that of impurities (such as silicon dioxide) affect the formation temperature of the slag.
.jpg)
Blast furnace is one of the most common smelting equipments in iron making process. The main raw materials of iron making include: iron ore, coke, limestone, air. The main composition of iron ore is various iron oxides. In the furnace, coke serves as a reducing agent and heat source. Meanwhile, carbon dissolves in molten iron to form pig iron (with a high carbon content of approximately 2-4%). During production, iron ore, coke and slag flux (limestone) are loaded from the furnace top, and preheated air is blown into the furnace tuyere located in the lower part of the furnace along the furnace. Under high temperatures, the carbon in coke (some blast furnaces also blow auxiliary fuels such as pulverized coal, heavy oil, natural gas, etc.) and the carbon monoxide and hydrogen generated by oxygen combustion into the air are removed from the oxygen in the iron ore during the rising process in the furnace, thus obtaining the iron after reduction.
.jpg)
.jpg)
According to previous project experience, the construction investment of the auxiliary system is 4 to 5 times that of the blast furnace body. In production, the various systems cooperate with each other and restrict each other to form a continuous, large-scale high-temperature production process. After the blast furnace is opened, the whole system must be continuously in production day and night, in addition to planned maintenance and special accidents, the furnace is generally stopped at the end of the life of the generation.
.jpg)
Pig iron refining process
The subsequent processes of pig iron refining are mainly aimed at adjusting the carbon content and removing impurities, thereby producing steel materials with different properties, such as steel or wrought iron. The main methods include: (1) Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steelmaking method (2) Electric Arc Furnace steelmaking method (EAF)